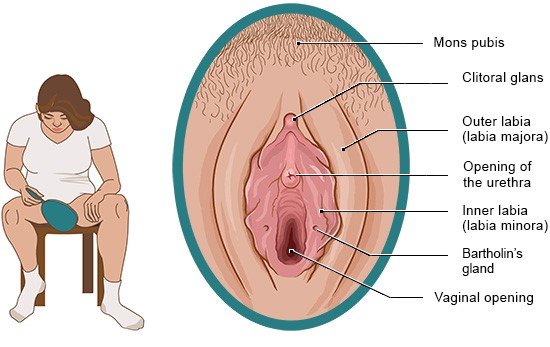
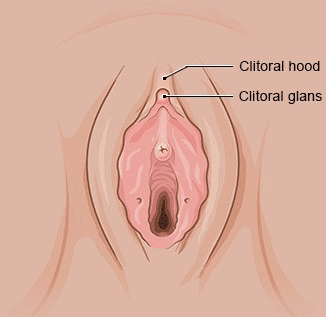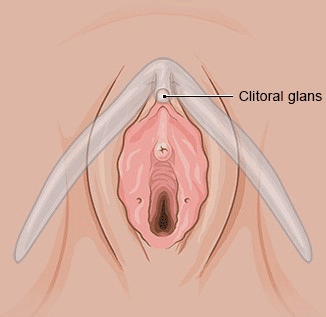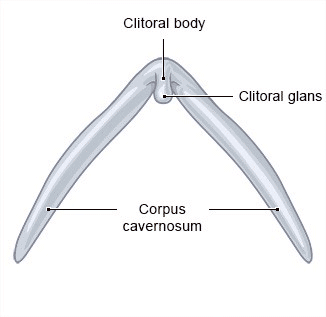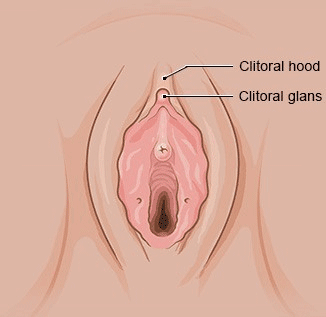
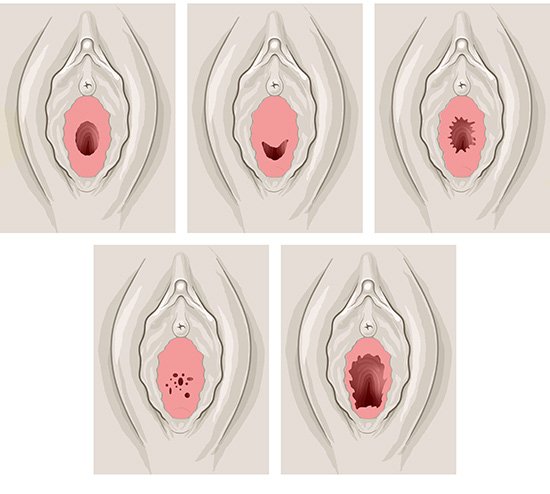
The hymen does make the vagina narrower more or less, but it is still possible for the blood of the monthly period to flow through it. Depending on the shape of the hymen, it can be torn by inserting a penis or sex toy. That could cause it to bleed, but it doesn't have to. After that, the hymen shrinks to down to a smaller size at the opening of the vagina, Some women and girls are born with a hymen that has a larger opening. So it is not possible to tell by the hymen whether a girl or woman has already had sex.
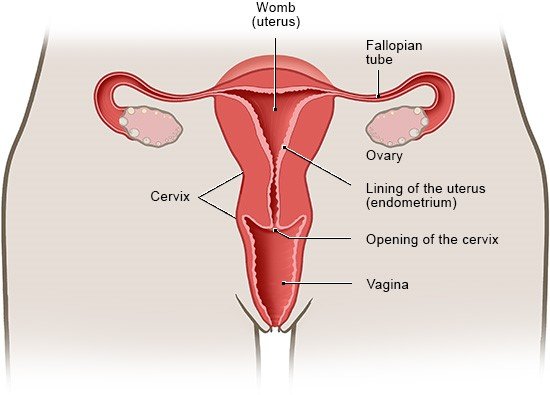
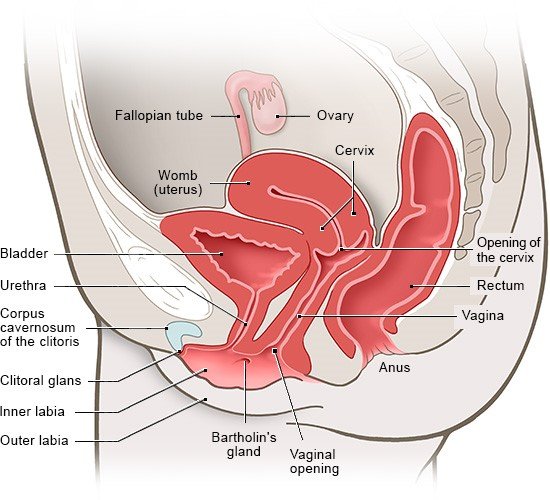
The womb (uterus) is roughly pear-shaped, and held in place in the pelvis by ligaments and muscles. The two fallopian tubes enter the upper, rounded end of the womb on the right and the left. The lower part of the womb is somewhat narrower, resembling the neck of a bottle. The lower end pushes slightly into the vagina. On the infertile days of the menstrual cycle, the opening of the cervix is closed by thick mucus.
The inside of the womb is lined with special membranes called the endometrium. In each menstrual cycle, female sex stimulate the endometrium to grow into a thick layer with higher blood flow so it is prepared for a fertilized egg: The egg can then become implanted in the lining of the womb and grow into an embryo. If fertilization doesn't take place, the thick membrane tissue which has built up is shed and leaves the woman's body during her period. If a fertilized egg becomes implanted, then a pregnancy begins. The lining is then not shed and there is no menstruation. The womb expands as the child grows.
The two ovaries are located on the right and left sides of the abdomen, and contain the eggs. These eggs can be fertilized by male sperm. The ovaries also produce important female sex such as estrogen and progesterone, which – among other things – regulate the menstrual cycle.
The fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus: During ovulation one of the two ovaries releases a mature egg cell into the opening of the fallopian tube, which is attached to the ovary like a funnel and can receive the egg cell. The egg cell moves along the fallopian tube and into the womb. The egg cell can already be reached by a sperm cell and fertilized while it is still in the fallopian tube.