What are the treatment options for hemangiomas in children (infantile hemangiomas)?
Infantile hemangiomas only have to be treated if they might cause complications because they're especially large or in a difficult place. Then doctors usually recommend treatment with medications known as beta blockers. This stops the growth of the hemangioma.
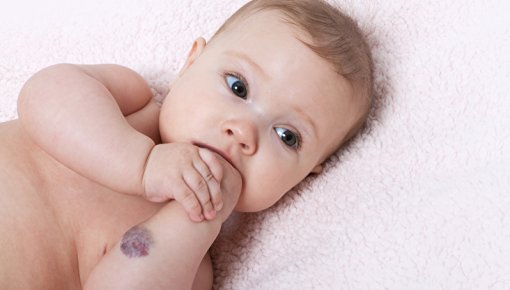
Infantile hemangiomas usually appear as red to purplish-blue marks or bumps, on or under the skin. They tend to be redder on light skin and more purple on dark skin. Commonly known as “strawberry birthmarks,” they often develop in the first few days or weeks of life. Most infantile hemangiomas don’t have to be treated because they don’t cause any problems and typically go away on their own by the age of ten at the latest.
But hemangiomas do sometimes cause complications or greatly affect your appearance. Then treatment is recommended.