The external female sex organs
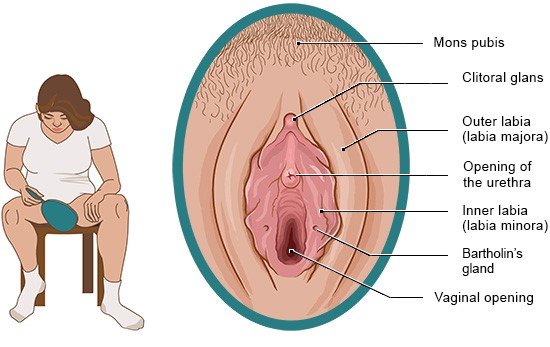
The external female sex organs include:
- Mons pubis (pubic mound)
- Outer labia (labia majora)
- Inner labia (labia minora)
- Clitoris
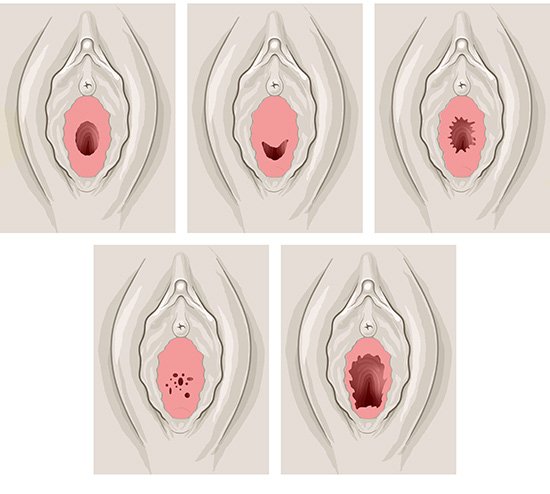
All of the parts of the external sex organs visible from the outside are called the vulva. Each vulva looks a little different, for instance the size and shape of the labia majora and the labia minora.
The mons pubis and the labia majora are cushioned with fat tissue and may be covered with (pubic) hair starting at puberty. These organs surround the labia minora, which are less cushioned and hairless. The opening of the vagina is between the labia minora. The skin and mucous membranes in this area have a lot of nerves and are very sensitive. As a result, touching and rubbing can cause sexual arousal that may lead to orgasm.
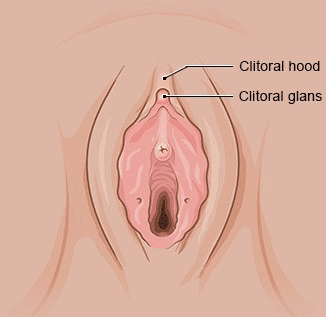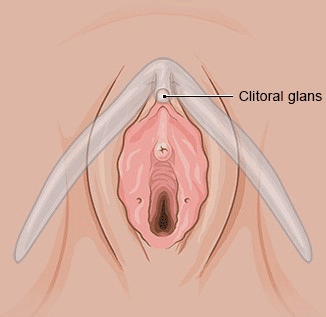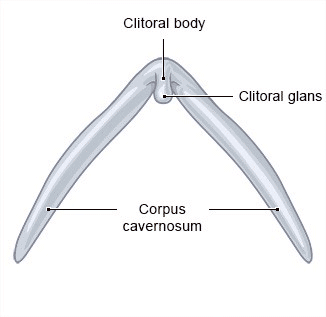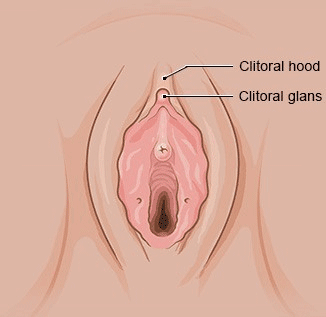
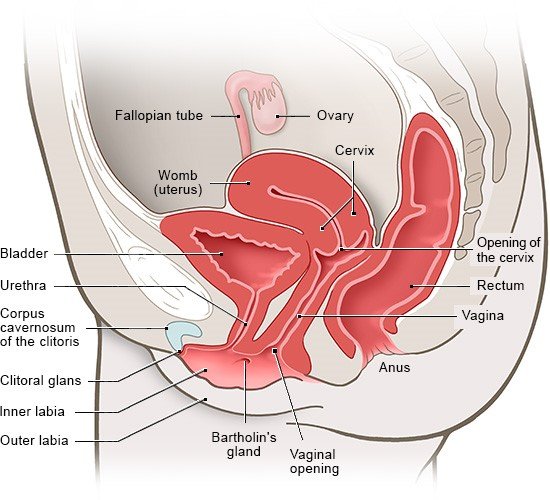
The clitoris is the main female organ for experiencing sexual pleasure. It consists of the head of the clitoris with a foreskin (clitoral hood), as well as the shaft and two “legs” with erectile structures (corpora cavernosa) that are positioned to the left and right of the urethra. The main part of the clitoris is located inside the body. Only the clitoral glans is visible from outside of the body, and also part of the clitoral body during sexual arousal.
The corpora cavernosa of the clitoris and of the vaginal vestibule are made of a sponge-like tissue. During sexual arousal, blood builds up in the corpora cavernosa until they are full and firm. This also causes the head and shaft of the clitoris to swell and stiffen. During an orgasm, the muscles beneath contract (tense) rhythmically.
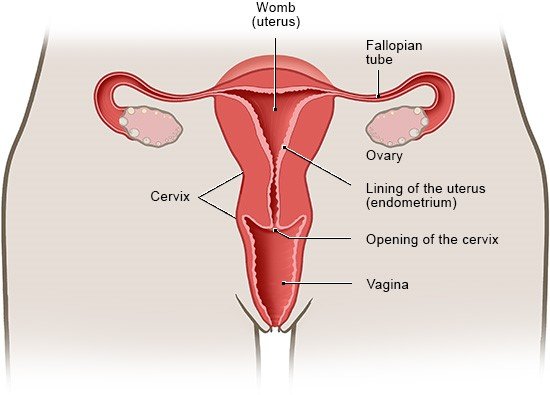
As soon as a woman is sexually aroused, the small Bartholin’s glands at the opening of the vagina release a fluid. The vagina becomes moist, making it easier for the penis to enter during sex. There may be other small glands near the urethra (Skene's glands). They have openings in the vaginal vestibule or near the opening of the urethra and also release a secretion during sexual arousal. The Bartholin's and Skene's glands are inside of the mucous membrane and not visible from outside the body, but they are still considered part of the external female sex organs.