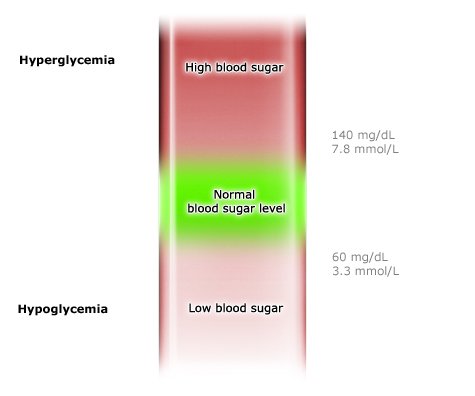
How is blood sugar measured?
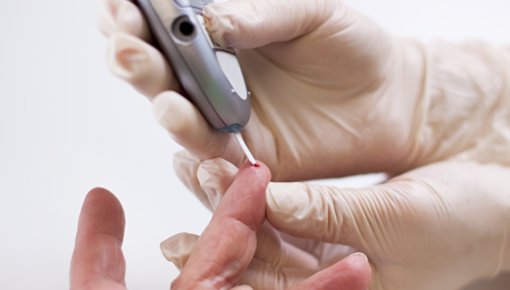
Many people with diabetes measure their blood sugar levels themselves. For those who inject insulin several times a day, checking their sugar levels is an important part of their daily treatment.
If someone has diabetes, their blood sugar levels are checked regularly. In type 2 diabetes, once every few months is sometimes enough. But not if insulin injections are part of their treatment. This is because the amount of insulin that is injected at mealtimes depends on the measured blood sugar level, among other things. Blood sugar levels can be measured in various ways. It is also possible to measure the level of sugar in tissues of the body.
You can learn how to measure your blood sugar yourself in special patient education classes. These are a part of diabetes disease management programs (DMPs) too.