Introduction

Syphilis is caused by bacteria. It is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) – like gonorrhea, chlamydia and trichomoniasis.
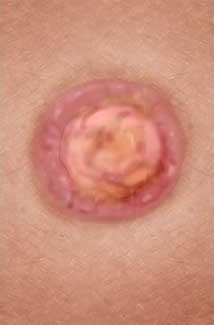
At the beginning of the infection, there is typically a single, painless sore (also known as a chancre) that heals on its own. Depending on where the bacteria got into the body, the sore forms on the penis, vagina, anus (bottom), lips or in the mouth.
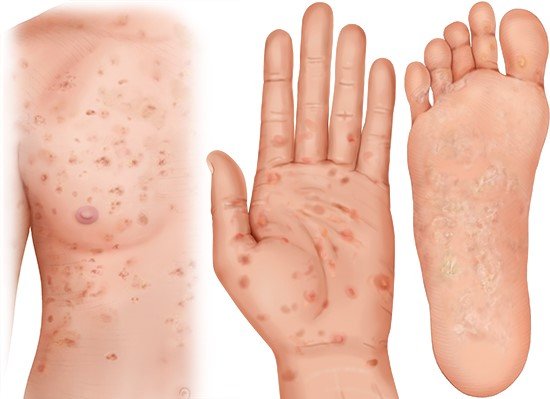
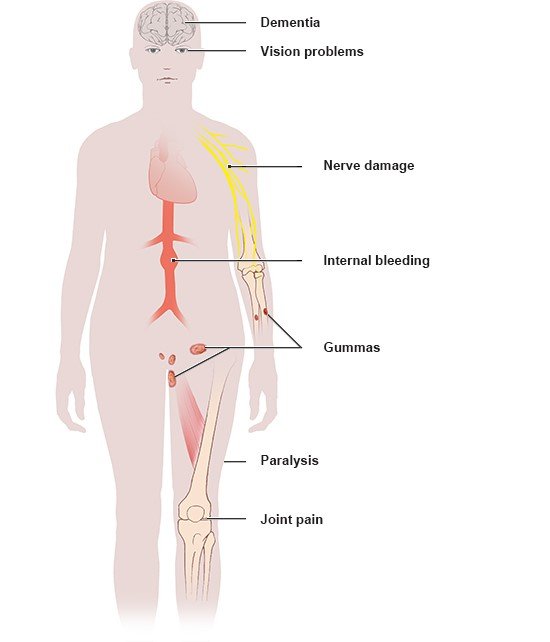
If left untreated, syphilis goes through various stages that may include a fever, sore throat, headache and rash. In the late stage, it can damage the aorta (main artery), the spinal cord or the brain and cause serious complications. Sometimes people have no symptoms for years between the stages. And many never have any symptoms at all. Then the disease may remain undetected and be unknowingly passed on to others.
Syphilis can be treated effectively with antibiotics. A long-acting penicillin drug is usually given as an injection. Other types of antibiotics can be used as well, though.