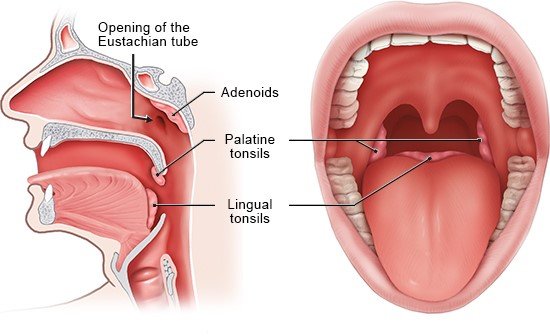
There are different types of tonsils:
- Palatine tonsils (tonsilla palatina)
- The adenoids (pharyngeal tonsil or tonsilla pharyngealis)
- Lingual tonsil (tonsilla lingualis)
The two palatine tonsils are found on the right and left of the back of the throat, and are the only tonsils that can be seen unaided when you open your mouth. The adenoids are found high up in the throat, behind the nose, and can only be seen through rhinoscopy (an examination of the inside of the nose). The lingual tonsil is located far back at the base of the tongue, on its back surface.
All of these tonsillar structures together are sometimes called Waldeyer's ring since they form a ring around the opening to the throat from the mouth and nose. This position allows them to prevent germs like viruses or bacteria from entering the body through the mouth or the nose. There are also more immune system cells located behind Waldeyer's ring on the sides of the throat. These cells can take on the function of the adenoids if they have been removed.
The palatine tonsils can become inflamed. Known as tonsillitis, this makes them swell up and turn very red. They often have yellowish spots on them as well. The most common symptoms are a sore throat and fever.
The palatine tonsils and the adenoids may become enlarged, especially in children. That makes it harder to breathe and causes sleep problems. Because of these problems, tonsil surgery is sometimes recommended.