Introduction

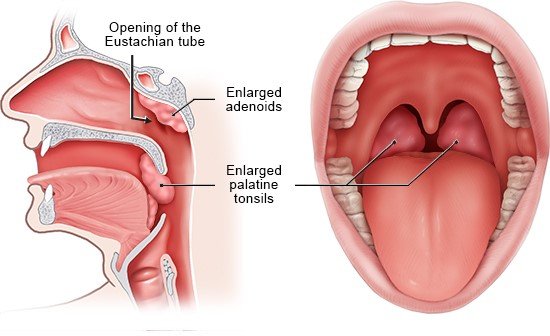
Many children have enlarged tonsils or adenoids. This can make their airways narrower, causing them to snore, stop breathing for short periods of time, and sleep poorly over the long term. Because of this, doctors often recommend surgery to remove the extra tissue.
Some children have enlarged palatine tonsils (often simply referred to as "tonsils," on the left and right sides at the back of the throat), and others have enlarged adenoids (also called the pharyngeal tonsil, found at the back of the nose). The medical terms for these enlarged areas of tissue are "tonsil hypertrophy" and "adenoid hypertrophy." Sometimes both are enlarged.
Adenoids are not to be confused with nasal polyps. These are benign growths in the membranes lining the nose. They usually only grow in adults. It is also important not to confuse enlarged tonsils with tonsillitis (an inflammation of the tonsils). These are two different medical conditions.