Introduction

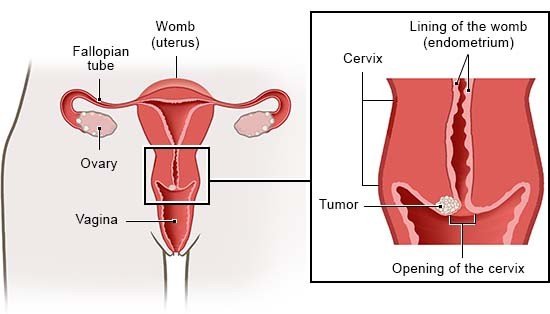
Cervical cancer causes tumors to develop on the cervix (the lower part of the womb). Cervical cancer is nearly always caused by an infection with human papillomaviruses (HPV). These viruses are spread during sex. The body can usually fight them off successfully, and the HPV infection doesn't cause any problems. But sometimes the viruses permanently remain in the lining of the cervix and lead to changes in the tissue there. That can result in cancer.
The HPV vaccine reduces the risk of being infected with the cancerous human papillomaviruses. The vaccination is currently recommended in Germany by the Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) at the Robert Koch Institute (RKI), and is also paid for by German public health insurers.
If you have already been infected, a screening test can detect possible tissue changes, which can then be removed. That prevents cancer from developing. If you already have cancer, there are various treatment options, regardless of how advanced the disease is or whether you still want to be able to get pregnant.