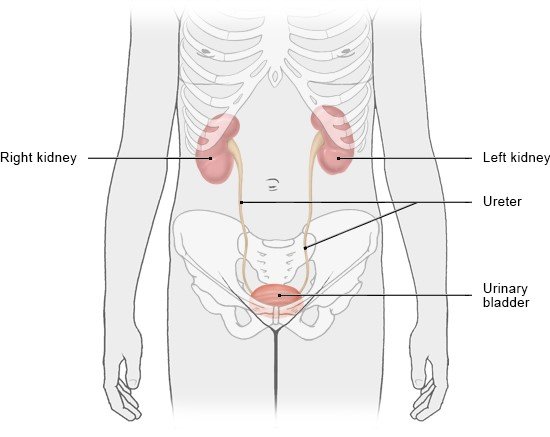
People usually have two kidneys, which look like oversized beans. The kidneys are located to the right and left of the spine, just below your ribcage.
Each kidney is about as big as a bar of soap or a clenched fist and weighs 135 to 150 grams. The indented side of the kidney faces inward toward the spine. In the middle of this indented side lies an area known as the renal hilum. This is where blood vessels, nerves and lymph vessels enter the kidney. It is also where urine leaves the kidney through the ureter.
Kidney structure
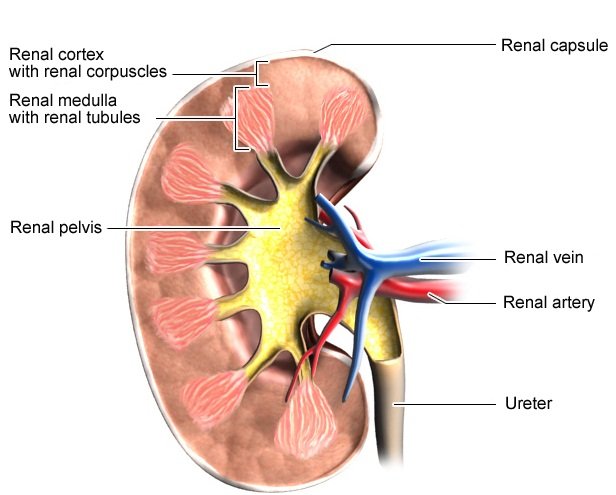
Each kidney is covered by three layers made out of fat or connective tissue, called the kidney capsule (or renal capsule). These layers give the kidney extra stability, protect it from injury from the outside, and attach it to the surrounding tissue.
The kidney is made up of two main parts: The outer layer is called the renal cortex. It has about 1.2 million renal corpuscles, which is where urine is produced. The renal medulla is found inside the kidney. Blood vessels and winding renal tubules run through the renal medulla. Urine passes through these renal tubules, then through the renal pelvis to the ureter, and then on to the urinary bladder.
What do the kidneys do?
The kidneys are our body’s sewage treatment plants: By producing urine that leaves the body, they get rid of waste products, such as urea, that form in the body or that we have consumed in food and drinks. Urea forms when proteins are metabolized (broken down by the body). The body is also able to get rid of medicine, drugs or toxins through urine.
Besides producing urine, the kidneys also have other important tasks. They regulate the body’s water balance by either holding back water or releasing excess water with the urine. When your kidneys hold back water, more fluid enters your blood vessels. The volume of blood increases, and your blood pressure rises. When your kidneys release more water, the volume of blood decreases and your blood pressure falls. There are also special cells in the kidneys that produce the protein renin. Renin has a hormone-like effect that increases blood pressure.
The kidneys also produce two important hormones called erythropoietin and calcitriol. Erythropoietin plays a role in the production of red blood cells. Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D and regulates things like the amount of calcium in the body.
The body's acid-base balance is also controlled by the kidneys. So the kidneys make sure that the blood doesn’t become too acidic or too alkaline. The body's energy metabolism is influenced by the kidneys as well: If there is too little sugar (glucose) in the blood, the kidneys can make sugar and release it into the bloodstream.
Each kidney has a pyramid-shaped gland “sitting” on it like a small hat, called the adrenal gland. These adrenal glands make several essential hormones, such as cortisol (also known as hydrocortisone).
Brandes R, Lang F, Schmidt R. Physiologie des Menschen: mit Pathophysiologie. Berlin: Springer; 2019.
Menche N. Biologie Anatomie Physiologie. München: Urban und Fischer; 2023.
Pschyrembel Online. 2025.
IQWiG health information is written with the aim of helping people understand the advantages and disadvantages of the main treatment options and health care services.
Because IQWiG is a German institute, some of the information provided here is specific to the German health care system. The suitability of any of the described options in an individual case can be determined by talking to a doctor. informedhealth.org can provide support for talks with doctors and other medical professionals, but cannot replace them. We do not offer individual consultations.
Our information is based on the results of good-quality studies. It is written by a team of health care professionals, scientists and editors, and reviewed by external experts. You can find a detailed description of how our health information is produced and updated in our methods.
Stay informed
Subscribe to our newsletter or newsfeed. You can find our growing collection of films on YouTube.