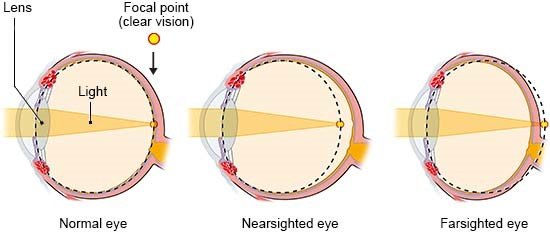
Fu Z, Hong H, Su Z et al. Global prevalence of amblyopia and disease burden projections through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Ophthalmol 2020; 104(8): 1164-1170.
Gesellschaft für Neuropädiatrie (GNP). Visuelle Wahrnehmungsstörungen (Sk2-Leitlinie). AWMF-Registernr.: 022-020. 2017.
Hashemi H, Pakzad RM, Yekta A et al. Global and regional estimates of prevalence of amblyopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Strabismus 2018; 26(4): 168-183.
Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG, Germany). Screening for visual impairment in children: Final report; Commission S05-02. 2008.
Jefferis JM, Connor AJ, Clarke MP. Amblyopia. BMJ 2015; 351: h5811.
Pschyrembel online. 2023.
West S, Williams C. Amblyopia in children (aged 7 years or less). BMJ Clin Evid 2016: 0709.
Zhang X, Wang J, Li Y et al. Diagnostic test accuracy of Spot and Plusoptix photoscreeners in detecting amblyogenic risk factors in children: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2019; 39(4): 260-271.
IQWiG health information is written with the aim of helping people understand the advantages and disadvantages of the main treatment options and health care services.
Because IQWiG is a German institute, some of the information provided here is specific to the German health care system. The suitability of any of the described options in an individual case can be determined by talking to a doctor. informedhealth.org can provide support for talks with doctors and other medical professionals, but cannot replace them. We do not offer individual consultations.
Our information is based on the results of good-quality studies. It is written by a team of health care professionals, scientists and editors, and reviewed by external experts. You can find a detailed description of how our health information is produced and updated in our methods.