What happens during cardiac catheterization?
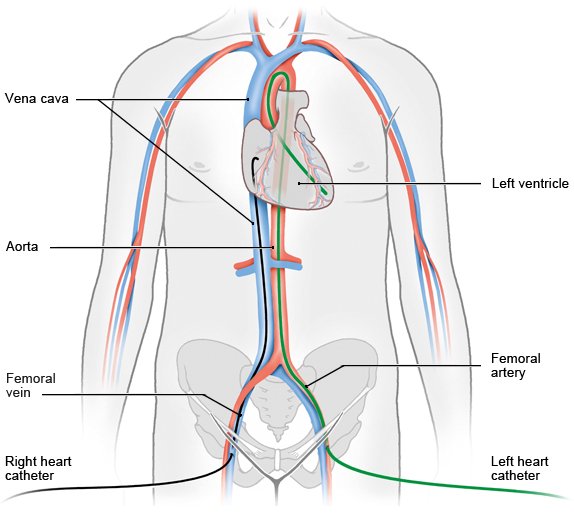
Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to show on a computer monitor diseases that affect the heart. A cardiac catheter is a thin, flexible tube. During catheterization, x-ray monitoring is used to guide the catheter through a blood vessel from the groin or arm to the heart.
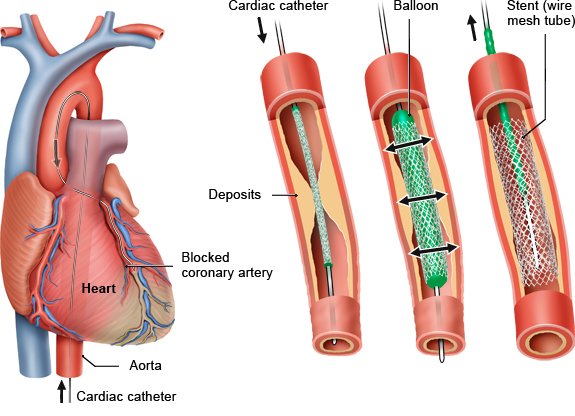
This procedure is often done to make the coronary arteries visible. The medical term for this is coronary angiography. Any narrowed blood vessels can be treated right away using the cardiac catheter.
The catheter may need to be advanced to the heart for other diseases – such as heart valve problems or an irregular heartbeat (cardiac arrhythmia). Then doctors are often able to treat the heart directly by using the catheter to put in a new heart valve or to carry out cardiac ablation, for example.