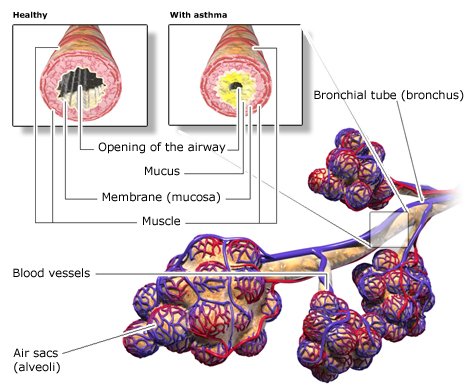
The main goal of asthma treatment depends on your own needs. It usually involves reducing the frequency and the severity of the symptoms as much as possible. The treatment should also help people with asthma to live as normal a life as possible. It is important to know that asthma treatment with medication has very few side effects. This is also the case for women with asthma who are pregnant. A doctor can help you decide which medications could be used.
Two main groups of medications are used to treat asthma:
- fast-acting medication that is taken when needed (reliever or “rescue” medication), and
- slow-acting medication that is taken regularly (controller or preventer medication).
If you have mild asthma, you may just need to use a reliever. Then you only take the medication when you have symptoms.
But more severe asthma can usually only be managed by using controller medication. These reduce the chronic inflammation in the airways, and this helps prevent asthma attacks. They are typically used on a daily basis. The choice of treatment always depends on how severe the symptoms are. The medication can only offer enough protection from asthma attacks if it is used consistently.
Trying to avoid contact with asthma triggers can help too. That's not always easy to do in daily life, though, and may sometimes be impossible. Finding out whether you are sensitive to animals, dust mites or cold air can be helpful. But avoiding those triggers doesn’t always prevent asthma symptoms from occurring. Most people who have asthma don’t need to worry too much about the triggers if they use their medication correctly.
Sports and exercise, as well as certain breathing techniques, can also help to keep the symptoms under control. Although these don’t usually work without using medication too, the two approaches complement each other well. It’s best to talk with your doctor about which treatments are most suited to reaching your goals.
It may also be a good idea to be vaccinated against the flu or pneumococci.