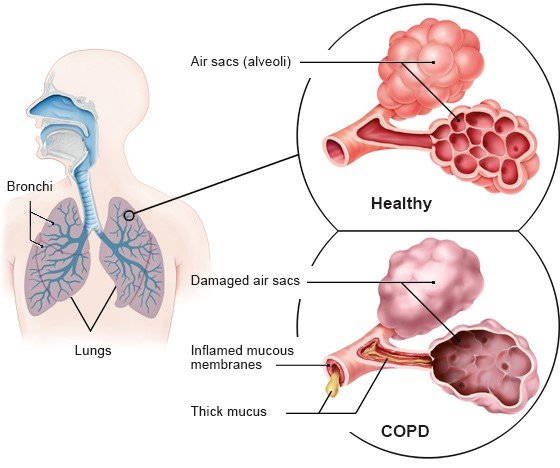
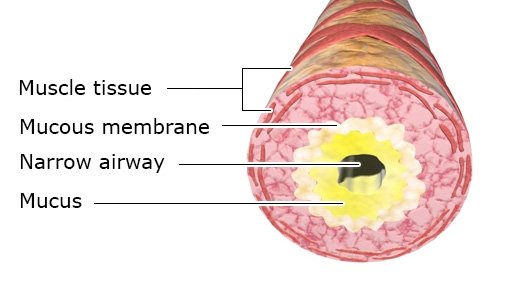
One aim of COPD treatment is to relieve symptoms, making everyday life easier and improving quality of life. A further aim is to slow down the progression of the disease and prevent exacerbations.
This most important thing that can be done is to stop smoking completely. This is often easier said than done. But there are various options for finding help, from online or telephone support and group courses to medication. Strategies for quitting include combining a support program and nicotine replacement therapy.
Other supportive measures include exercise and sports, breathing exercises, inhalation, and changes in diet. In Germany, statutory health insurers also offer disease management programs (DMPs) for people with COPD. The aim of these programs is to provide consistent treatment in close cooperation with medical professionals to reduce the number of severe flare-ups and slow down the progression of the disease.
If these non-medication options do not help enough, medication is an essential part of daily COPD treatment. It is typically inhaled (breathed in), but can also be taken in the form of tablets. Depending on how far the disease has progressed, combinations of various drugs can be used, either as a long-term treatment or temporarily to relieve acute symptoms. The following medications are available:
- Drugs that open up (dilate) the airways (bronchodilators): These drugs are typically inhaled as a powder or spray to make it easier to breathe. They include beta-2 agonists and anticholinergics.
- Phosphodiesterase (PDE) 4 inhibitors reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Steroid medication also has an anti-inflammatory effect, but are usually only considered if the symptoms are very severe.
- In rare cases, antibiotics can be used temporarily for prevention.
At very advanced stages of COPD, oxygen therapy is often needed as well.
If all other treatment options for severe pulmonary emphysema have been tried out, surgery is possible as well. Then the overinflated parts of the lungs are reduced in size through a procedure called bullectomy or through lung volume reduction surgery. A lung transplant may even be considered in some situations.